Structure and content
Structure of the study programme
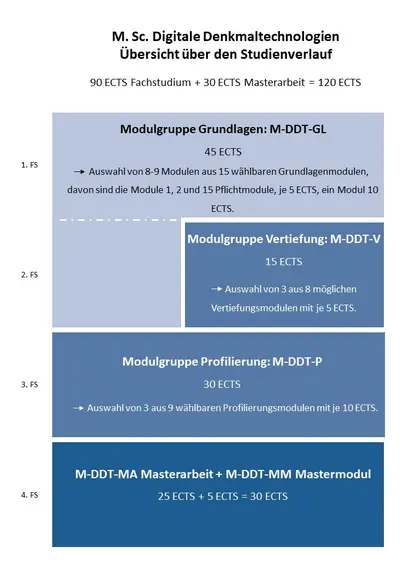
The subject study programme consists of fourmodule groups with different objectives, fundamentals, in-depth studies/ advanced modules, profiling and Master's thesis with a topic and professor of your choice (who is also authorized and teaching on this Masters program, see below).
In the first study section, students take eight or nine from a total of 15 basic modules. These modules are intended to supplement existing knowledge in order to create a foundation for subsequent deepening and application.
In the next section, electives are taken in three in-depth modules (out of eight possible) and three consecutive profiling (specialisation) modules(depending on previous choices for advanced module ) , which allow students to choose between several subject fields in which they can acquire in-depth knowledge, in-depth assessment skills and practical and applied competence while developing their own research approaches.
Module group: basics
Students receive introductions to subjects relevant to the application of digital technologies in heritage conservation. In the basics modules you should acquire 45 ECTS (credit points). Each of the modules has 5 ECTS , with the exception of GL-6 (10 ECTS).
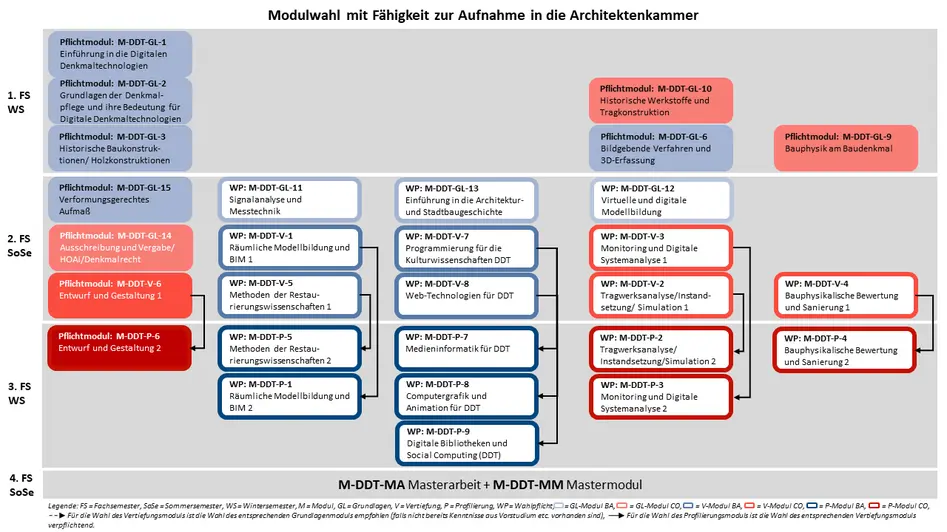
- M-DDT-GL-1 Introduction to Digital Technologies in Heritage Conservation
- M-DDT-GL-2 Principles and Theories of Heritage Conservation and their Significance for Digital Heritage Technologies
- M-DDT-GL-3 Historic Building/Wooden Constructions
- M-DDT-GL-4 Technical Drawing and Computer-aided Design (CAD)
- M-DDT-GL-5 Computer Science for Students from the Humanities
- M-DDT-GL-6 Digital Object Recording and Digital Imaging Technologies
- M-DDT-GL-7 Digital Archiving and Digital Humanities
- M-DDT-GL-8 Introduction to Building Preservation Sciences
- M-DDT-GL-9 Building Physics for Heritage Buildings
- M-DDT-GL-10 Historic Materials and Introduction to Structural Engineering
- M-DDT-GL-11 Signal Analysis and Measurement Technology
- M-DDT-GL-12 Digital Modelling of 3D Spatial Data and Data Analysis
- M-DDT-GL-13 Introduction to History of Architecture and Building.
- M-DDT-GL 14 Tender and Awarding in Construction/ HOAI/ Heritage Law
- M-DDT-GL 15 As-built drawing of historic buildings
The modules M-DDT-GL-1 Introduction to Digital Technologies in Heritage Conservation, M-DDT-GL-2 Principles and Theories of Heritage Conservation and their Significance for Digital Heritage Technologies and M-DDT-GL-15 As-built drawing of historic buildings are compulsory modules, all others are elective. These three modules provide an overview of the subjects involved in the degree programme as well as a foundation for acquiring more specialist knowledge in of Digital Technologies in Heritage Conservation.
More flexibility in the study programme
Are you an archaeologist who would like to learn digital surveying methods but shy away from building physics? Are you an art historian who would like to digitise the museum landscape, but don't know your way around computer science?
With the new study examination regulations, you can tailor your studies more individually to your needs and interests without necessarily having to cover all areas. You can get a taste of everything and find your own individual path. The programs’ student advisory service of this masters will be happy to support you.
Chamber of architects eligibility (German list of architects)
Prerequisite for entry in the list of architects specialising in architecture in the Bavarian Chamber of Architects according to Art. 4 (2) BauKaG
You have studied architecture in the Bachelor's programme, but you are still lacking ECTS to become eligible for the Chamber of Architects? With the new study examination regulations, you can achieve the requirements for entry into the list of architects with our Masters in Digital Technologies in Heritage Conservation degree programme.
What do you need to do? There are a number of modules whose enrolment is agreed with the Chamber of Architects. If you study according to the following scheme, you will automatically receive confirmation for the Chamber of Architects with your certificate. An individual examination at the Chamber of Architects is then no longer necessary. After two years of professional practice, you can then register with the Chamber.
You take all the basic modules marked "compulsory module" in red in the diagram (this means you have already completed the required 45 ECTS of the basic modules, but you are also welcome to attend other basic modules on a voluntary basis), as well as the specialisation M-DDT-V-6 ‘Architectural Design and Layout 1’ and the profiling M-DDT-P-6 ‘Architectural Design and Layout 2’. You can then freely choose two further specialisations and profiling. The Master's thesis should then be written across the board of topics, so that as many areas of the degree course as possible are included (including, for example, design).