Structure and Curriculum
Students in the German Linguistics master’s programme choose from two programme tracks based on two specialisations. The degree programme is research-oriented and leads to a second professional-level qualification in the subject of German Linguistics in four semesters.
Holders of a qualified master's degree are eligible to enrol in doctoral studies and obtain the title of Dr. phil. at the University of Bamberg.
Both specialisation tracks – Systematic and Historical Linguistics and German as a Foreign Language – share two core modules: German Linguistics I and German Linguistics II. The other modules focus on the topics and methods relevant to their respective pathway. For clarity, they are listed separately in the following overview.
German Linguistics I and German Linguistics II
These modules teach advanced theoretical and methodological skills in analysing concrete linguistic phenomena and the ability to apply those skills to new research topics.
MA German Linguistics – Systematic and Historical Linguistics specialisation
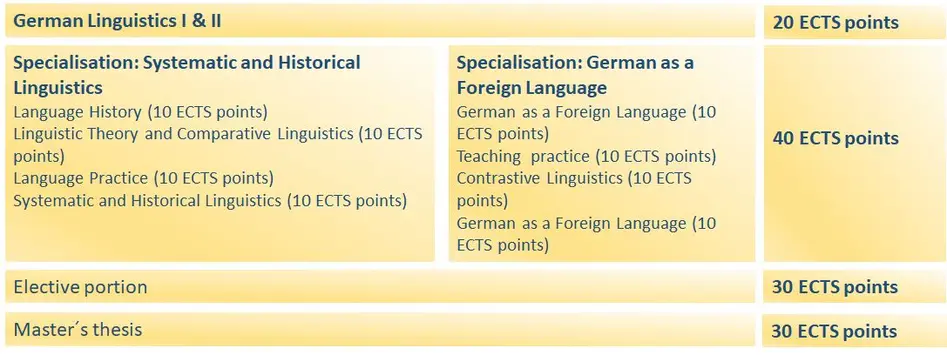
- 20 ECTS points in 2 core modules: German Linguistics I and German Linguistics II;
- 10 ECTS points in the module Language History;
- 10 ECTS points in the module Linguistic Theory and Comparative Linguistics;
- 10 ECTS points in the module Language Practice
- 10 ECTS points in the specialisation module Systematic and Historical Linguistics, in which students write their master's thesis.
The Systematic and Historical Linguistics specialisation track consists of the modules Historical Linguistics, Linguistic Theory and Comparative Linguistics and Language Practice. This combination of modules ensures that students acquire key qualifications in synchronic, historical and contrastive linguistics. During the seminars, the contents and methods of the various modules are put into mutual context in order to help students practise their transfer skills and to provide value in terms of theories and content.
MA German Linguistics – German as a Foreign Language specialisation
- 20 ECTS points in 2 core modules: German Linguistics I and German Linguistics II;
- 10 ECTS points in the module German as a Foreign Language;
- 10 ECTS points in the module Teaching Practice;
- 10 ECTS points in the module Contrastive Linguistics;
- 10 ECTS points in the specialisation module for German as a Foreign Language, in which students write their master's thesis.
The German as a Foreign Language specialisation track consists of the modules German as a Foreign Language, Teaching Practice and Contrastive Linguistics. This combination of modules ensures that students acquire and apply didactic and methodological skills, analyse the structure of a foreign language as compared to German, reflect on the results from a teaching perspective and explore additional aspects of linguistics that are relevant to teaching German, such as theories of first/second/foreign-language acquisition and intercultural communication.
Master's Thesis
Both specialisation tracks include a specialisation module, which encourages students to explore a research question in their chosen specialism in depth and prepares them for writing their master's thesis.
The master's thesis is an independently written work which showcases the student's advanced understanding of their subject and their ability to apply academic methods to concrete research issues within a limited time frame. Master’s students in German Linguistics normally write their master's thesis immediately after their third semester. The thesis must be completed within six months.
Distribution Electives
For the elective portion of their degree, students select individual aspects of their subject to study in greater depth or explore another subject, for example, economics or psychology. The modules chosen for the elective portion must add up to at least 30 ECTS points. They can be selected from a minor subject which the students is already studying or from any other subject. The module ‘German Linguistics III’ is also available as an elective module. Alternatively, students can fulfil the elective portion of their degree by spending a semester at another university in German or abroad. The elective portion can also be used to catch up on missing basic knowledge. Other options may be considered.
Module Handbook
For further details on the structure and timeline of the German Linguistics master’s programme and the content of its modules, see the module handbook.